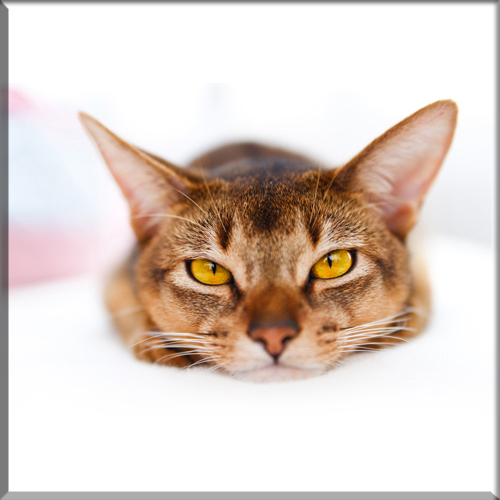
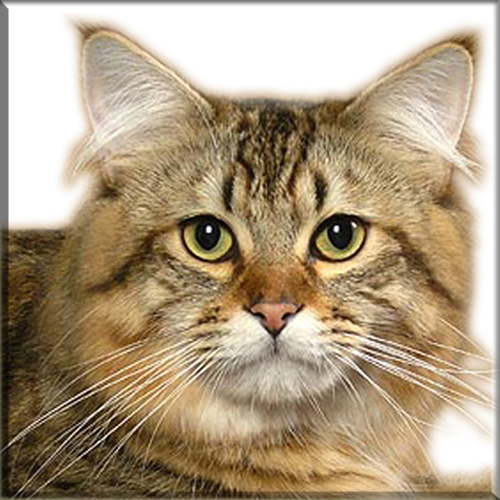
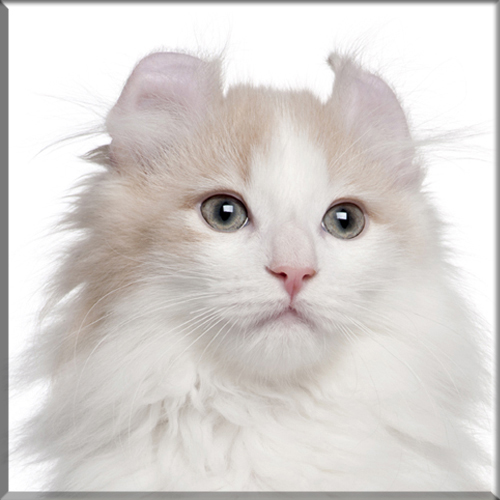
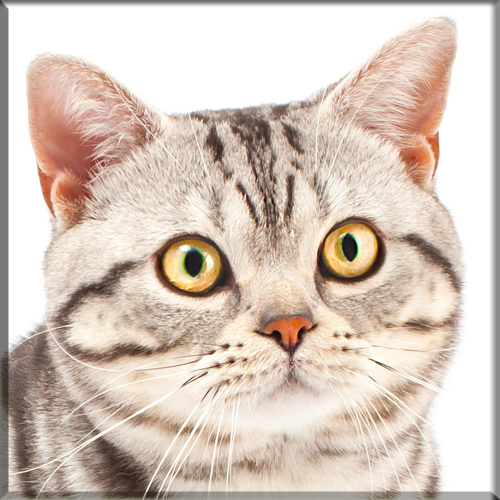
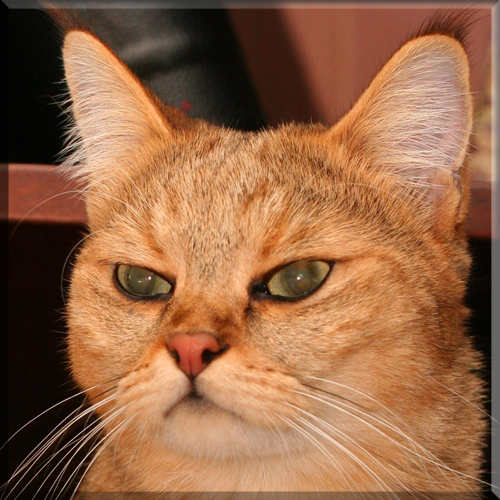
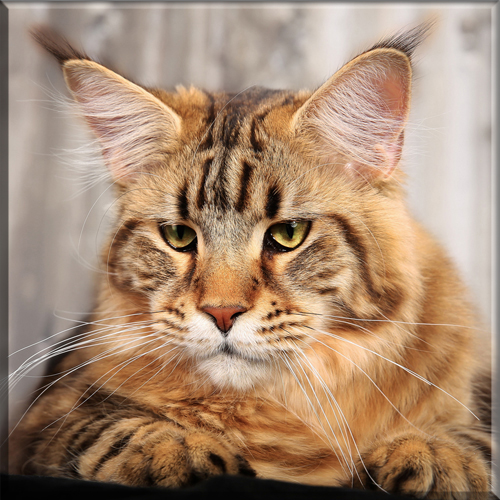
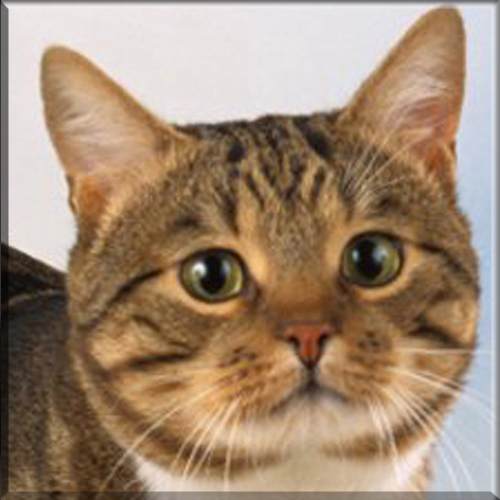
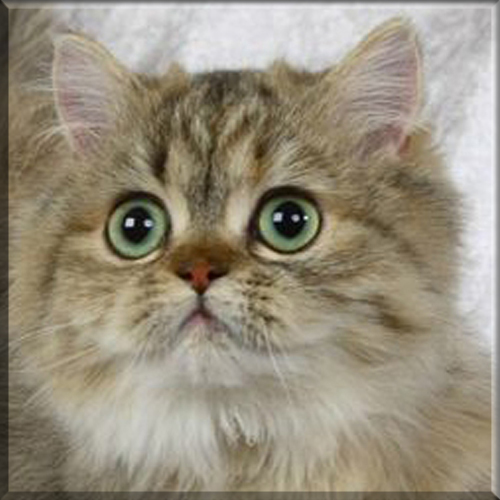
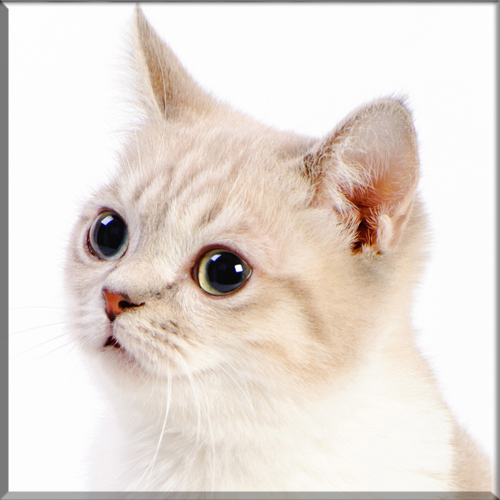
Pixie Bob
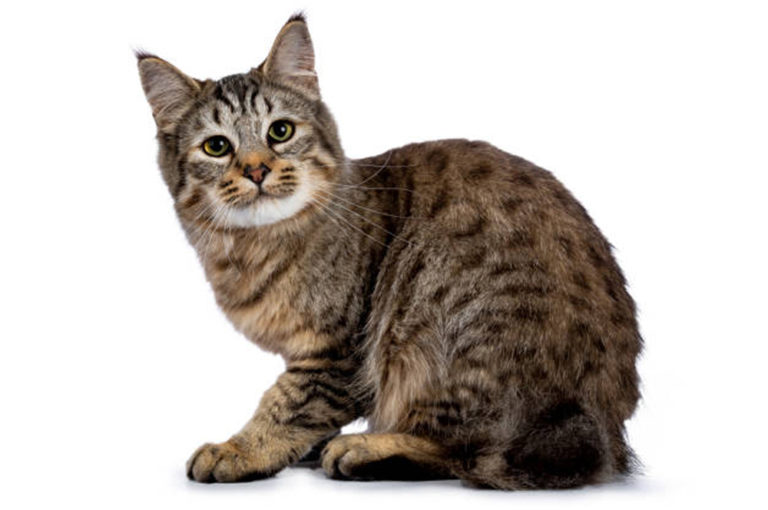

Appearance and features:
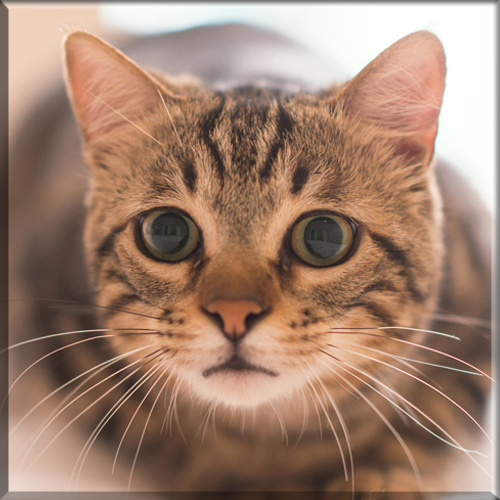
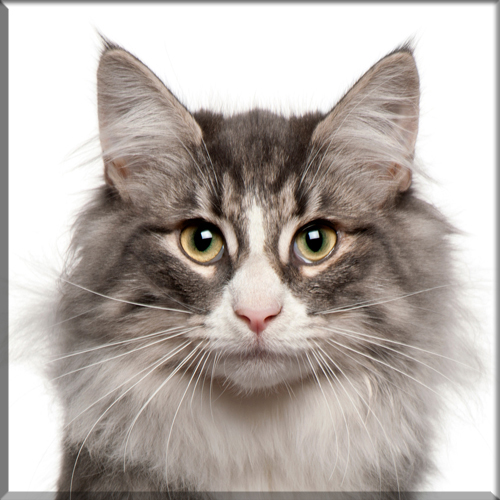
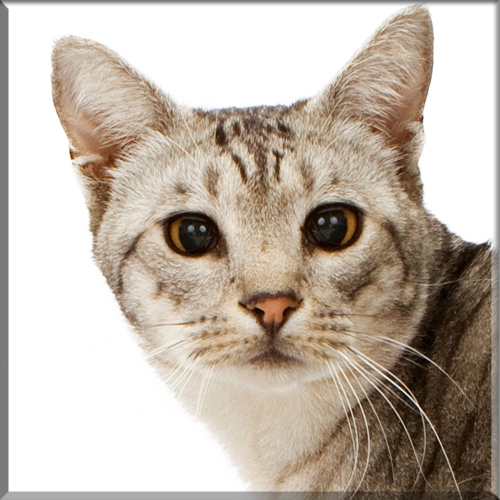
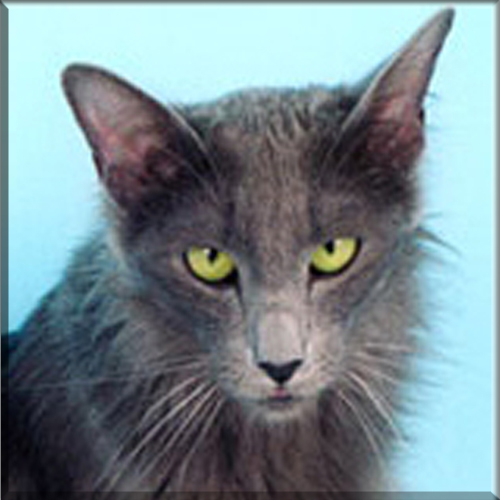
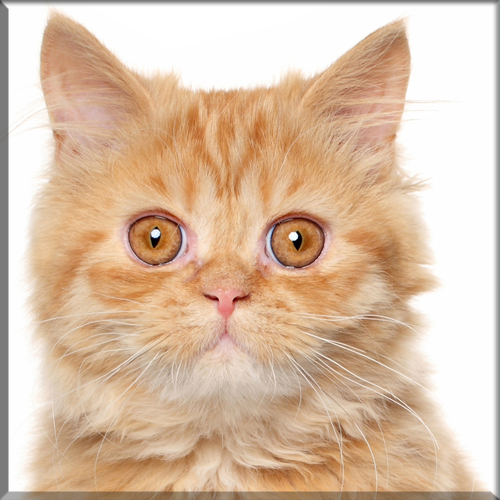
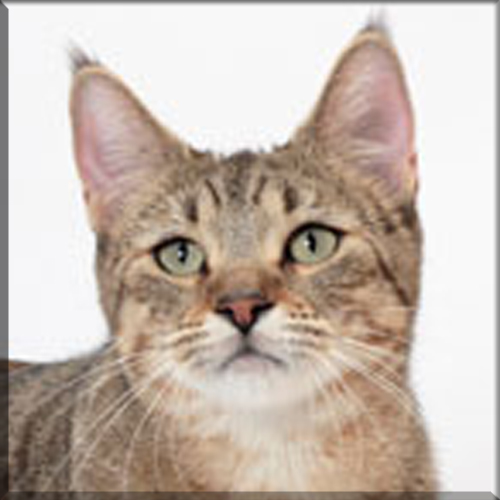
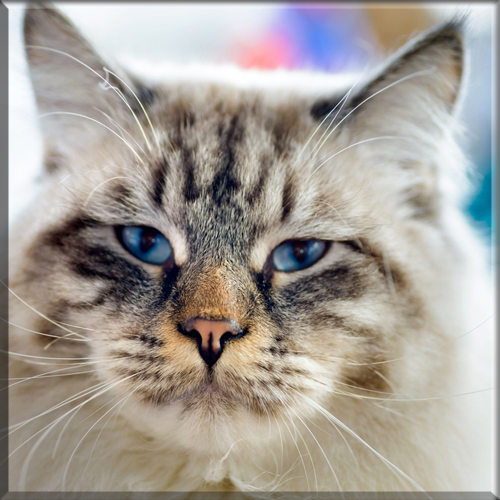
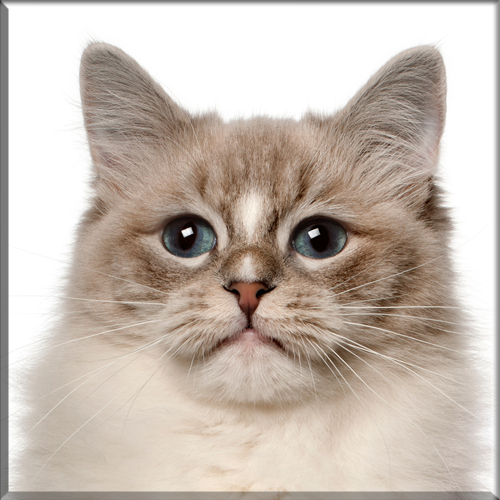
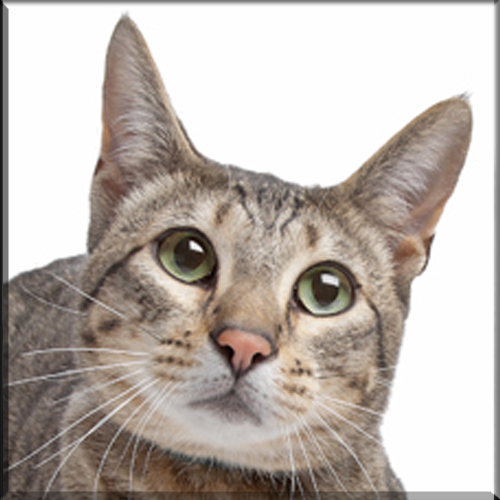
Most Pixie-bobs have black fur and skin on the bottom of their paws, tipped ears, heavy ear hair, black lips, and white fur around the eyes but with black eye skin. Their chins have white fur, but often have black skin under the white fur. Some of their whiskers change from black (root – about 25%) to white (to the tip – about 75% of the whisker). Bobcat-like fur pattern, but often have reddish tones mixed in. Most are short-haired, but some are long-haired. The brow should be heavy and the eyes should have a triangular shape. Eyes are blue when kittens, then change to green or gold when several months old. Tails can be non-existent (rumpy), or 2-4 inches (5–10 cm) (desired – TICA required), or long tails (StoneIsland Pixie was a long-tail). The head is pear shaped. The head is considered to be the most important characteristic.
Size:
Family:
Coloring:
Origin:
In the spring of 1985, Carol Ann Brewer purchased near Mount Baker, Washington, a unique male cat with a spotted coat, a short tail, and polydactyl paws. In January 1986, she rescued another male cat named Keba, which was very large, had a bobbed tail, and was reported to have been sired by a bobcat. While this cat was starving, it still weighed 17 pounds, and was so tall it reached up to Brewer’s knees. Shortly after she had acquired this large male, it mated with a next door neighbors brown spotted female cat. In April 1986, a litter was born from this mating. Brewer eventually kept one of the female kittens, named “Pixie”, and after a year started a breeding program with Pixie as the foundation cat.
Over the next couple of years, Brewer introduced into her program 23 cats from around the nearby Cascade range, that were believed by her to be born from naturally occurring matings between bobcats and domestic cats. She coined the term “Legend Cat” to refer to such cats and has since registered a trademark in the U.S. to limit the term to describe permitted outcrosses used in her breeding program. At the same time, other breeders in the U.S. were working with distinctly wild looking barn cats and collaborated with Brewer to establish a broad genetic base and to develop the foundation of today’s Pixie-bob.
Temperament:
Pixie-bobs are said to be highly intelligent, social, active, bold, and enjoy playing with other animals. They are also known for their “chirps”, chatters, and growls; most do not meow often, and some do not meow at all.
Most Pixie-bobs are highly sociable around both their owners and strangers. Almost all Pixie-bobs like to be in the same room as their owners, and will follow their owners around the house.
Other personality characteristics include the following:
- Head butting
- Ball fetching and playing
- Leash walking (for the most part)
- Highly intelligent
- Capable of understanding some human words and phrases
Health concerns:
Some rare genetic diseases includes the following:
- Cryptorchidism – only a few cases have been recorded, since the conception of this breed in the 1980s.
- Dystocia and cystic endometrial hyperplasia – A very small percentage of Pixie-bobs do suffer from delivery problems, and are removed from breeding.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) – Since the advent of the Pixie-bob breed in the 1980s, only a few cases have been reported. In some of those cases the Pixie-bob was cross-bred with other breeds of cats, such as Bengal and Maine Coon. In the majority of cases, HCM occurred spontaneously. HCM is hereditary in at least 50% of occurrences necessitating annual ultrasound screens to confirm continued health of the cats.
Breed Characteristics
Here is a helpful guide for the different characteristics of the breed. On a Scale of 1-5. 1 being very low level to 5 being high level.
Hypoallergenic: No

Breeders With Currently Available Kittens
All The Cat Breeds
- Abyssinian
- American Bobtail
- American Curl
- American Shorthair
- American Wirehair
- Balinese
- Bengal
- Birman
- Bombay
- British Shorthair
- Burmese
- Burmillia
- Charteux
- Chausie
- Colorpoint Shorthair
- Cornish Rex
- Devon Rex
- Donskoy
- Egyption Mau
- European Burmese
- Exotic
- Havana Brown
- Highlander
- Himalayan
- Japanese Bobtail
- Khao Manee
- Korat
- LaPerm
- Lykoi
- Maine Coon
- Manx
- Minuet / Napolean
- Munchkin
- Norwegian Forest Cat
- Ocicat
- Oriental Longhair
- Oriental Shorthair
- Persian
- Peterbald
- Pixie Bob
- Ragamuffin
- Ragdoll
- Russian Blue
- Savannah
- Scottish Fold
- Scottish Straight
- Selkirk Rex
- Seychellois
- Siamese
- Siberian
- Singapora
- Snowshoe
- Somali
- Sphynx
- Thai
- Tonkinese
- Toyger
- Turkish Angora
- Turkish Van