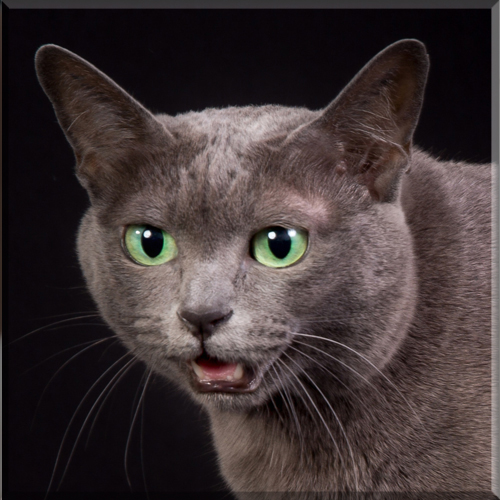
Korat

Appearance and features:
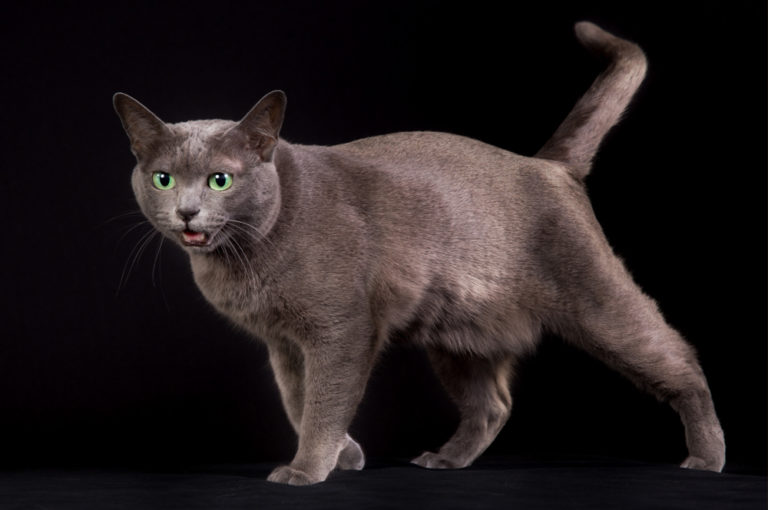
The Korat is a silver-tipped blue-grey, short-haired breed of domestic cat with a small to medium build and a low percentage of body fat. Its body is semi-cobby, and unusually heavy for its size. It is an intelligent and playful active cat that forms strong bonds with people. Among the Korat’s distinguishing characteristics are its heart-shaped head and large green eyes.
Size:
Family:
Coloring:
Origin:
The probable first allusion to the breed is in the Thai Tamra Maew (The Cat-Book Poems), authored between 1350 and 1767 CE and now in the National Library of Thailand.[1] However, the illustration of the Korat in this book is not detailed enough to be definitive as to the breed portrayed. In recent years, the Korat was pictured on a postage stamp in Thailand. An example hangs in the city of Korat’s post office.
Korats first appeared in Britain under the name “Blue Siamese” in 1889 and 1896, but these solid blue cats did not conform to the cat show judges’ perception of a Siamese cat, and they disappeared by 1901. One early import, “Dwina”, owned by Russian Blue breeder Mrs. Constance Carew-Cox and mentioned in Frances Simpson’s The Book of the Cat (1903), reputedly produced a large number of “Siamese” kittens; the other, Mrs. B. Spearman’s Blue Siamese male, “Nam Noi”, was disqualified as a Siamese, but accepted in the Russian or Any Other Blue class in which he placed first (WR Hawkins, “Around the Pens”, July 1896). Spearman tried unsuccessfully to import more of these “Blue Siamese”.
Korats first appeared in the US in the 1950s. In 1959, Cedar Glen cattery was the first to import a pair of Korats to the US for breeding: a male named Nara and a female named Darra. In 1966, the Korat was accepted into championship status, through the efforts of a breeder from Maryland.
Temperament:
Health concerns:
Korats can have a genetic neuromuscular degenerative disease as well as low body fat, which can make them sensitive to anesthesia.
GM1 and GM2 gangliosidosis occur when cats lack particular enzymes that are necessary for proper functioning of the nervous system. Fortunately, tests are available to identify cats that carry the diseases, so the condition is uncommon.
Breed Characteristics
Here is a helpful guide for the different characteristics of the breed. On a Scale of 1-5. 1 being very low level to 5 being high level.
Hypoallergenic: No

Breeders With Currently Available Kittens
All The Cat Breeds
- Abyssinian
- American Bobtail
- American Curl
- American Shorthair
- American Wirehair
- Balinese
- Bengal
- Birman
- Bombay
- British Shorthair
- Burmese
- Burmillia
- Charteux
- Chausie
- Colorpoint Shorthair
- Cornish Rex
- Devon Rex
- Donskoy
- Egyption Mau
- European Burmese
- Exotic
- Havana Brown
- Highlander
- Himalayan
- Japanese Bobtail
- Khao Manee
- Korat
- LaPerm
- Lykoi
- Maine Coon
- Manx
- Minuet / Napolean
- Munchkin
- Norwegian Forest Cat
- Ocicat
- Oriental Longhair
- Oriental Shorthair
- Persian
- Peterbald
- Pixie Bob
- Ragamuffin
- Ragdoll
- Russian Blue
- Savannah
- Scottish Fold
- Scottish Straight
- Selkirk Rex
- Seychellois
- Siamese
- Siberian
- Singapora
- Snowshoe
- Somali
- Sphynx
- Thai
- Tonkinese
- Toyger
- Turkish Angora
- Turkish Van